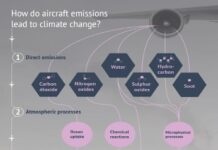
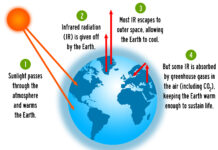
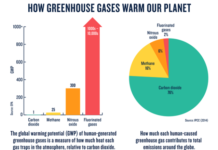
Greenhouse gases (GHGs) have both natural and human-created sources.
Natural sources include respiration and decomposition of plants and the ocean release of greenhouse gases to the atmosphere. Many natural GHGs occur naturally in the atmosphere, such as water vapor, carbon dioxide, methane and nitrous oxide.
Other greenhouse gases are synthetic i.e. human-made, include chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs), hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs), perfluorocarbons (PFCs) and sulphur hexafluoride (SF6).
Currently, human emissions of GHGs into the atmosphere has reached 50 billion tonnes on an annual basis, [measured in carbon dioxide equivalents (CO2eq)]. [1]Carbon dioxide-equivalents try to sum all of the warming impacts of the different greenhouse gases together in order to give a single measure of total greenhouse gas emissions. To convert non-CO2 … Continue reading
Many countries, sectors, and processes contribute to these global emissions. This means there is no single or simple solution to tackle climate change – there will need to be many solutions.
Greenhouse Emissions Trend, Starting with 1990 as the Baseline
To most effectively reduce emissions we need to understand emission sources and then determine the methods and technologies required to rapidly reduce and eliminate them. The figure below shows the breakdown of global greenhouse gas emissions in 2016, by sector. [2] While it would be ideal to have more timely data, this is the most recent data available at time of writing (September 2020). This was published by the Climate Watch and the World Resources Institute. [3] The World Resources Institute also provides a nice visualization of these emissions as a Sankey flow diagram.
Annual Greenhouse Gas Emissions By Sector, CY 2016
The graphic shows that almost ~75% of emissions come from energy use; ~20% to ~25% from agriculture, land use, processing, packaging, transport and retail; and the remaining ~8% from industry and waste.
A short description of each sector is included below and is based on explanations provided in the IPCC’s Fifth Assessment Report AR5) and a methodology paper published by the World Resources Institute.
Energy (electricity, heat and transport): 73.2%
Energy use in industry: 24.2%
- Iron and Steel (7.2%): Energy-related emissions from the manufacturing of iron and steel.
- Chemical & petrochemical (3.6%): Energy-related emissions from the manufacturing of fertilizers, pharmaceuticals, refrigerants, oil and gas extraction, etc.
- Food and tobacco (1%): Energy-related emissions from the manufacturing of tobacco products and food processing (the conversion of raw agricultural products into their final products, such as the conversion of wheat into bread).
- Non-ferrous metals: 0.7%: Non-ferrous metals are metals which contain very little iron: this includes aluminium, copper, lead, nickel, tin, titanium and zinc, and alloys such as brass. The manufacturing of these metals requires energy which results in emissions.
- Paper & pulp (0.6%): Energy-related emissions from the conversion of wood into paper and pulp.
- Machinery (0.5%): Energy-related emissions from the production of machinery.
- Other industry (10.6%): Energy-related emissions from manufacturing in other industries including mining and quarrying, construction, textiles, wood products, and transport equipment (such as car manufacturing).
Transport: 16.2%
This includes all direct emissions from burning fossil fuels to power transport activities and a small amount of electricity (from indirect emissions) as well. These figures do not include emissions from the manufacturing of motor vehicles or other transport equipment – this is included in the previous point ‘Energy use in Industry’.
- Road transport (11.9%): Emissions from the burning of petrol and diesel from all forms of road transport which includes cars, trucks, lorries, motorcycles and buses. Sixty percent of road transport emissions come from passenger travel (cars, motorcycles and buses); and the remaining forty percent from road freight (lorries and trucks). This means that, if we could electrify the whole road transport sector, and transition to a fully decarbonized electricity mix, we could feasibly reduce global emissions by 11.9%.
- Aviation (1.9%): Emissions from passenger travel and freight, and domestic and international aviation. 81% of aviation emissions come from passenger travel; and 19% from freight.7 From passenger aviation, 60% of emissions come from international travel, and 40% from domestic.
- Shipping (1.7%): Emissions from the burning of petrol or diesel on boats. This includes both passenger and freight maritime trips.
- Rail (0.4%): emissions from passenger and freight rail travel.
- Pipeline (0.3%): Fuels and commodities (e.g. oil, gas, water or steam) often need to be transported (either within or between countries) via pipelines. This requires energy inputs, which results in emissions. Poorly constructed pipelines can also leak, leading to direct emissions of methane to the atmosphere – however, this aspect is captured in the category ‘Fugitive emissions from energy production’.
Energy use in buildings: 17.5%
- Residential buildings (10.9%): Energy-related emissions from the generation of electricity for lighting, appliances, cooking etc. and heating at home.
- Commercial buildings (6.6%): Energy-related emissions from the generation of electricity for lighting, appliances, etc. and heating in commercial buildings such as offices, restaurants, and shops.
Unallocated fuel combustion (7.8%)
- Energy-related emissions from the production of energy from other fuels including electricity and heat from biomass; on-site heat sources; combined heat and power (CHP); nuclear industry; and pumped hydroelectric storage.
Fugitive emissions from energy production: 5.8%
- Fugitive emissions from oil and gas (3.9%): Fugitive emissions are the often-accidental leakage of methane to the atmosphere during oil and gas extraction and transportation, from damaged or poorly maintained pipes. This also includes flaring – the intentional burning of gas at oil facilities. Oil wells can release gases, including methane, during extraction. Producers often don’t have an existing network of pipelines to transport Methane, or it wouldn’t make economic sense to provide the infrastructure needed to effectively capture and transport it. But under environmental regulations they need to deal with it somehow: intentionally burning it is often a cheap way to do so.
- Fugitive emissions from coal (1.9%): Fugitive emissions are the accidental leakage of methane during coal mining.
Energy use in agriculture and fishing (1.7%)
- Energy-related emissions from the use of machinery in agriculture and fishing, such as fuel for farm machinery and fishing vessels.
Direct Industrial Processes: 5.2%
- Cement (3%): carbon dioxide is produced as a byproduct of a chemical conversion process used in the production of clinker, a component of cement. In this reaction, limestone (CaCO3) is converted to lime (CaO), and produces CO2 as a byproduct. Cement production also produces emissions from energy inputs – these related emissions are included in ‘Energy Use in Industry’.
- Chemicals & petrochemicals (2.2%): greenhouse gases can be produced as a byproduct from chemical processes – for example, CO2 can be emitted during the production of ammonia, which is used for purifying water supplies, cleaning products, and as a refrigerant, and used in the production of many materials, including plastic, fertilizers, pesticides, and textiles. Chemical and petrochemical manufacturing also produces emissions from energy inputs – these related emissions are included in ‘Energy Use in Industry’.
Waste: 3.2%
- Wastewater (1.3%): Organic matter and residues from animals, plants, humans and their waste products can collect in wastewater systems. When this organic matter decomposes it produces methane and nitrous oxide.
- Landfills (1.9%): Landfills are often low-oxygen environments. In these environments, organic matter is converted to methane when it decomposes.
Agriculture, Forestry and Land Use: 18.4%
- Agriculture, Forestry and Land Use directly accounts for 18.4% of greenhouse gas emissions. The food system as a whole – including refrigeration, food processing, packaging, and transport – accounts for around one-quarter of greenhouse gas emissions. We look at this in detail here.
- Grassland (0.1%): When grassland becomes degraded, soils can lose carbon, converting to carbon dioxide in the process. Conversely, when grassland is restored (for example, from cropland), carbon can be sequestered. Emissions here refer to the net balance of these carbon losses and gains from grassland biomass and soils.
- Cropland (1.4%): Depending on the management practices used on croplands, carbon can be lost or sequestered into soils and biomass. This affects the balance of carbon dioxide emissions. CO2 can be emitted when croplands are degraded; or sequestered when they are restored. The net change in carbon stocks is captured in emissions of carbon dioxide.
- Deforestation (2.2%): Net emissions of carbon dioxide from changes in forestry cover. This means reforestation is counted as ‘negative emissions’ and deforestation as ‘positive emissions’. Net forestry change is therefore the difference between forestry loss and gain. Emissions are based on lost carbon stores from forests and changes in carbon stores in forest soils.
- Crop burning (3.5%): The burning of agricultural residues – leftover vegetation from crops such as rice, wheat, sugar cane, and other crops – releases carbon dioxide, nitrous oxide and methane. Farmers often burn crop residues after harvest to prepare land for the resowing of crops.
- Rice cultivation (1.3%): Flooded paddy fields produce methane through a process called ‘anaerobic digestion’. Organic matter in the soil is converted to methane due to the low-oxygen environment of water-logged rice fields. The high 1.3% number is due to the fact that rice is a staple crop for billions of people globally and accounts for around one-fifth of the world’s supply of calories.
- Agricultural soils (4.1%): Nitrous oxide – a strong greenhouse gas – is produced when synthetic nitrogen fertilizers are applied to soils. This includes emissions from agricultural soils for all agricultural products – including food for direct human consumption, animal feed, biofuels and non-food crops (such as tobacco and cotton).
- Livestock & manure (5.8%): Animals (mainly ruminants, such as cattle and sheep) produce greenhouse gases through a process called ‘enteric fermentation’ – when microbes in their digestive systems break down food, they produce methane as a by-product. This means beef and lamb tend to have a high carbon footprint, and eating less is an effective way to reduce the emissions. Nitrous oxide and methane is produced from the decomposition of animal manures under low oxygen conditions. This often occurs when large numbers of animals are managed in a confined area, as in industrial farming e.g., dairy farms, beef feedlots, and swine and poultry farms, where manure is typically stored in large piles or disposed of in lagoons and other types of manure management systems. ‘Livestock’ emissions include direct emissions from livestock only.
References
| ↑1 | Carbon dioxide-equivalents try to sum all of the warming impacts of the different greenhouse gases together in order to give a single measure of total greenhouse gas emissions. To convert non-CO2 gases into their carbon dioxide-equivalents we multiply their mass (e.g. kilograms of methane emitted) by their ‘global warming potential’ (GWP). GWP measures the warming impacts of a gas compared to CO2; it basically measures the ‘strength’ of the greenhouse gas averaged over a chosen time horizon. |
|---|---|
| ↑2 | While it would be ideal to have more timely data, this is the most recent data available at time of writing (September 2020). |
| ↑3 | The World Resources Institute also provides a nice visualization of these emissions as a Sankey flow diagram. |